The Army Futures Command’s (AFC) Future Vertical Lift (FVL) Cross-Functional Team (CFT)’s 2024 iteration of the Experimental Demonstration Gateway Event (EDGE) concluded earlier this week after three weeks of experimentation.
EDGE 24 was deliberately smaller in scale than previous iterations of the event and focused on autonomous collaborative behaviors of unmanned aerial systems (UAS), launched effects (LE), and unmanned ground vehicles.
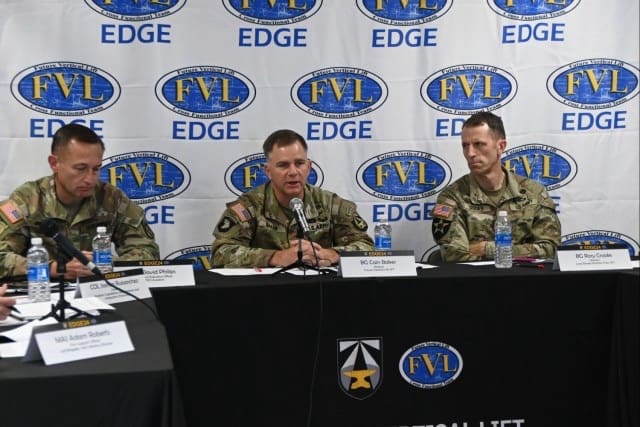
“Our specific experimental objective was learning how launched effect surrogates behave on a network and off a network,” said Brig. Gen. Cain Baker, FVL CFT Director. “Based off a simulated enemy threat array, we allowed the launched effect surrogates to operate on a network and pass information back at extended ranges, then deliberately removed the network to see if the autonomy could continue. We experimented with that very specifically and had a lot of success in the information we captured and the behaviors we saw from platforms from multiple vendors that were out here.”
The behaviors within launched effects provide a decisive advantage to ground commanders, giving them the capability to extend the range of sensing and use machines instead of Soldiers to make first contact with an adversary. The Army is rapidly integrating layered UAS and LE across formations in a combined arms fight that is synchronized with fires and maneuver across phases to penetrate, exploit, and defeat near-peer adversaries in a complex environment.
“We know looking into the future that we are going to be operating in congested airspace: there will be a number of friendly and adversary platforms that will exist in that space,” said Brig. Gen. William Parker, Director of the Air and Missile Defense CFT. “Reducing the cognitive burden on the operator and helping us deconflict what is in the air with respect to friendly and adversary capabilities will go a long way in how we fight that small UAS threat while protecting friendly UAS in that same airspace.”
The FVL CFT sees EDGE providing the Army Futures Command an experimentation and demonstration platform to help deliver the Army of 2030 and design of Army of 2040, and has chosen U.S. Army Yuma Proving Ground (YPG) as its venue for the last two years. The proving ground’s clear, stable air and extremely dry climate combined with an ability to control a large swath of the radio frequency spectrum makes it a desired location for the type of testing EDGE was interested in: counter-unmanned aircraft solutions, extending network access, and flying autonomous and semi-autonomous aircraft. YPG’s wealth of other infrastructure meant for other sectors of the post’s test mission were utilized to support the demonstration, including technical and tactical targets.
“YPG was essential for us to have the simulated threat array to conduct the experiment in at echelon that would replicate an enemy capability that we would potentially face in the future,” said Baker. “YPG has the air space that allows us to operate at the distances we need and the instrumentation to collect the data to inform our requirements from an analytical standpoint.”
YPG’s deep institutional knowledge allowed the participating industry partners to run complex test scenarios each day across three weeks of demonstrations, and the event paid dividends that could inform the Army for years to come. One industry partner exercised autonomous collaboration between an Unmanned Aerial System (UAS) and an Unmanned Ground Vehicle (UGV) through real-time aerial mapping of an urban environment to deliver a recommended route for the UGV to follow. Another successfully executed an automated target hand off between a UAS with a radio frequency sensor and a UAS with an electro optical infrared sensor. The demonstration also saw a long-range data communications relay of over 250 miles to execute a strike from a surrogate lethal long range launched effect.
“We’re seeing autonomy advance year after year when we do events like EDGE and Project Convergence,” said Baker. “If we operate these effects en masse, how do we offload the requirements for operators to control from one controller to one vehicle versus one controller for multiple vehicles? How do we share information about the battlefield rapidly and accurately, and how do we do that at extended ranges so crews can maximize the mission set they’re faced with?”
By Mark Schauer
Both comments and pings are currently closed.
Read the full article here







Leave a Reply